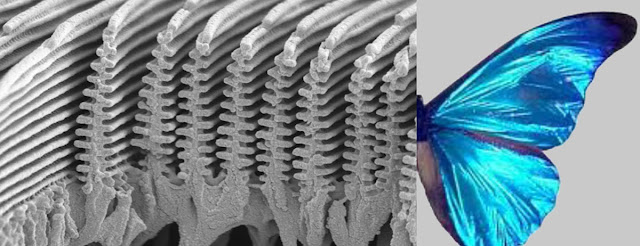
Butterfly wings are covered in scales that are made of a protein called chitin. These scales give butterfly wings their color, patterns, and texture. The colors of butterfly wings are created by the reflection, absorption, and transmission of light by the scales, pigments, and structures on the wings. The patterns and shapes of butterfly wings are determined by the arrangement and interaction of these scales, pigments, and structures. Some butterfly species have wings that are specifically adapted for camouflage, courtship, or thermoregulation.
https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/15440478.2022.2164107
Chitin
Chitin is a natural polymer that is found in the exoskeletons of crustaceans, insects, and other arthropods, as well as in the cell walls of fungi. It is composed of repeating units of a sugar called N-acetylglucosamine, linked together by glycosidic bonds. Chitin is the second most abundant biopolymer on earth after cellulose.
The use of chitin has been explored for various applications such as wound healing, drug delivery, tissue engineering, agriculture and food industries, cosmetics and personal care, environmental applications and more
Chitin Fiber

Chitin fiber is a natural polymer fiber derived from chitin There are several methods of producing chitin fibers, including mechanical, chemical and enzymatic methods. The most common method is the mechanical method, which involves grinding the chitin-rich shells of crustaceans into a powder, and then spinning the powder into fibers using a spinning machine. In chemical method, chitin is dissolved in a solvent, and then spinning the solution into fibers, this method can be used to produce chitin fibers in large amounts. In enzymatic method, chitin is first deproteinated by removing the protein content and then the fibers are produced by using the enzyme chitinase.The resulting fibers are strong, flexible, and have good moisture-wicking properties, making them suitable for use in textiles, such as clothing, bedding, and other applications.It is worth to mention that the production of chitin fibers is still a research area, it is not yet fully commercialized
Why Chitin Fiber
Chitin, as a fiber, offers several benefits over synthetic fibers and other natural fibers such as cotton and wool. Some of the main benefits are:
- Biodegradable: Chitin fibers are biodegradable and therefore do not contribute to the pollution caused by synthetic fibers.
- Biocompatible: Chitin is a natural material that is biocompatible, which means it does not cause any adverse reactions in the human body, making it safe for use in clothing and other applications.
- Strong and flexible: Chitin fibers are strong and flexible, which makes them suitable for use in textiles, such as clothing, bedding, and other applications.
- Moisture-wicking properties: Chitin fibers have good moisture-wicking properties, meaning they are able to absorb and transport moisture away from the skin, which can help to keep the wearer cool and comfortable.
- Antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties: chitin and chitosan fibers have been shown to have antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties, which can help to keep the wearer healthy and reduce the risk of infection.
- UV-protection: chitosan fibers have been reported to have UV-protection properties, which can protect the skin from the harmful effects of UV radiation.
Hope you learned something new. Till next time take care, wear mask and #SwachhBharat









 So in this series of articles / blogs we have discussed various factors which have influence in determining the thermal protection performance of a protective fabric and subsequently clothing.
So in this series of articles / blogs we have discussed various factors which have influence in determining the thermal protection performance of a protective fabric and subsequently clothing.